|
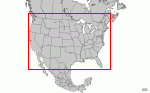
United States Range Map |
|
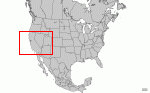
California Range Map |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Identification: |
|
Life history:
|
|
One tail on
hindwing. Upperside blue-gray with large red spot
near tail. Underside of spring/fall form is dark gray,
summer form is paler gray. Relatively straight postmedian
line is white, bordered with orange on the inside edge. |
|
Males perch all afternoon on small trees and shrubs to seek
receptive females. Eggs are laid singly on flowers of host
plant. Young caterpillars feed on flowers and fruits; older
ones may eat leaves. Chrysalids hibernate. |
|
Flight: |
|
Wing Span: |
|
Two flights from May-September in the north, three-four
flights from February-November in the south. |
|
7/8 - 1 3/8 inches (2.2 - 3.5 cm). |
|
Caterpillar Hosts: |
|
Adult Food: |
|
Flowers and fruits from an almost endless variety of plants;
most often from pea (Fabaceae) and mallow (Malvaceae)
families including beans (Phaseolus), clovers (Trifolium),
cotton (Gossypium), and mallow (Malva). |
|
Nectar from many flower species including dogbane, milkweed,
mint, winter cress, goldenrod, tick trefoil, and white sweet
clover. |
|
Habitat: |
|
Season: |
|
Open, nonforested sites; common in disturbed, weedy areas. |
|
Two flights from May-September in the north, three-four
flights from February-November in the south. |
|
Remarks: |
|
Conservation: |
|
The most widespread hairstreak in North America. |
|
Conservation: Not usually required.
NatureServe Global Status:
G5 - Demonstrably secure globally, though it may be quite
rare in parts of its range, especially at the periphery.
Management needs: Caterpillars may cause economic
damage to bean and cotton crops.
|
|
Sources used to
Construct this Page: |
|
|
|
|