|
|
|
 |
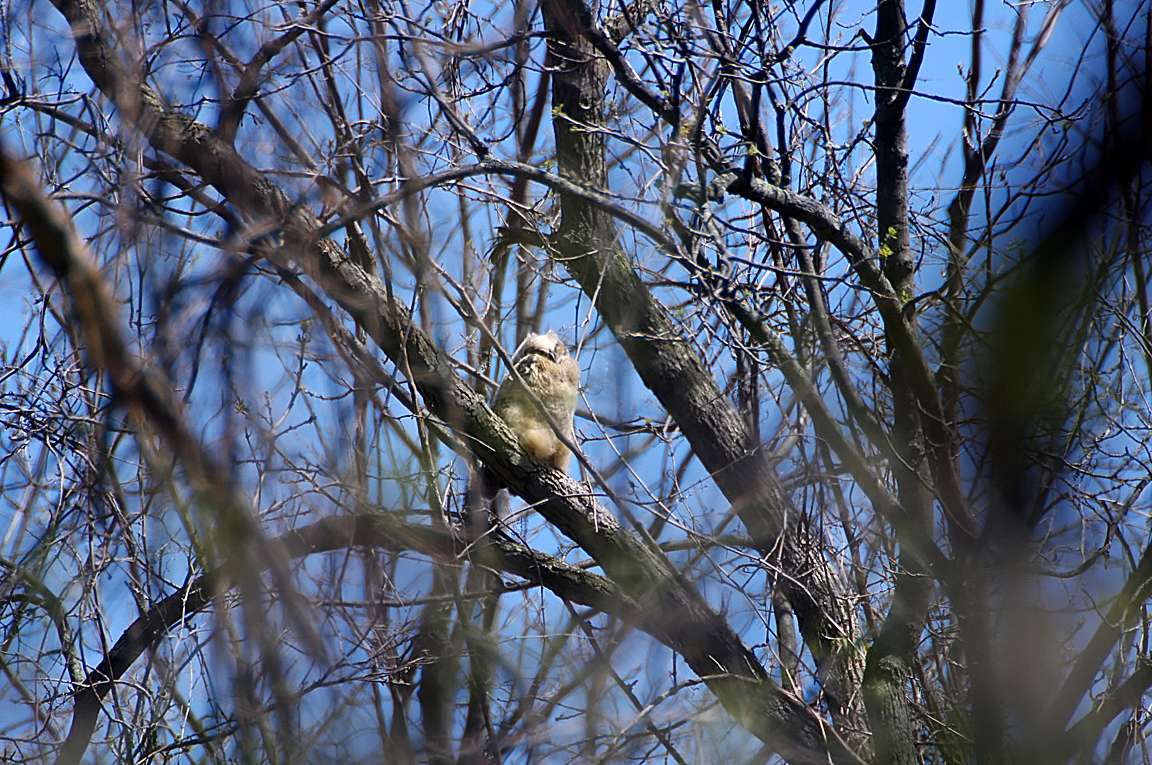
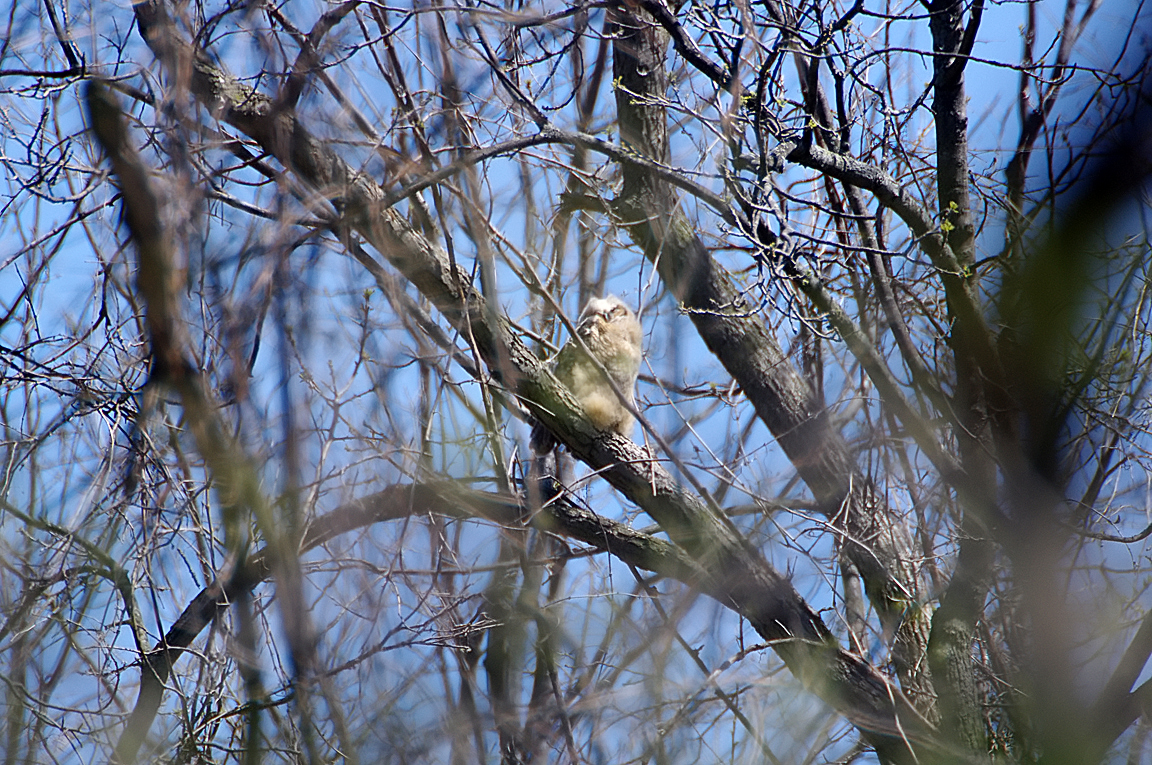
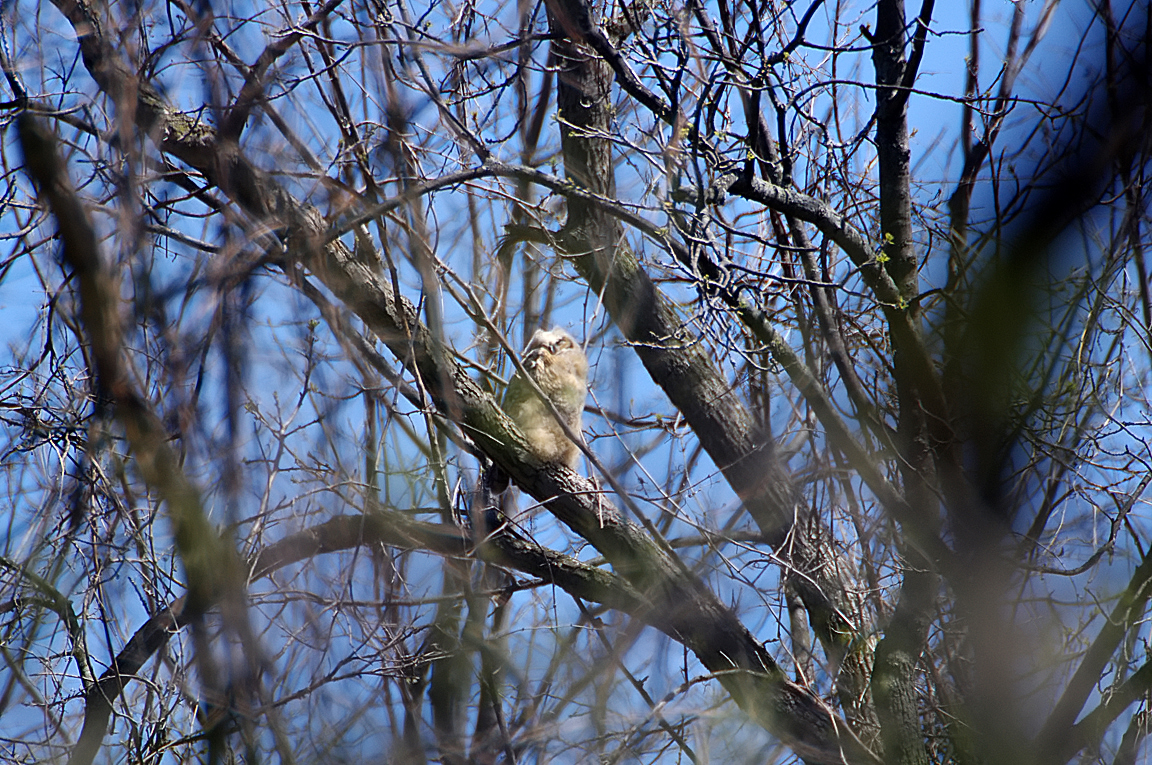
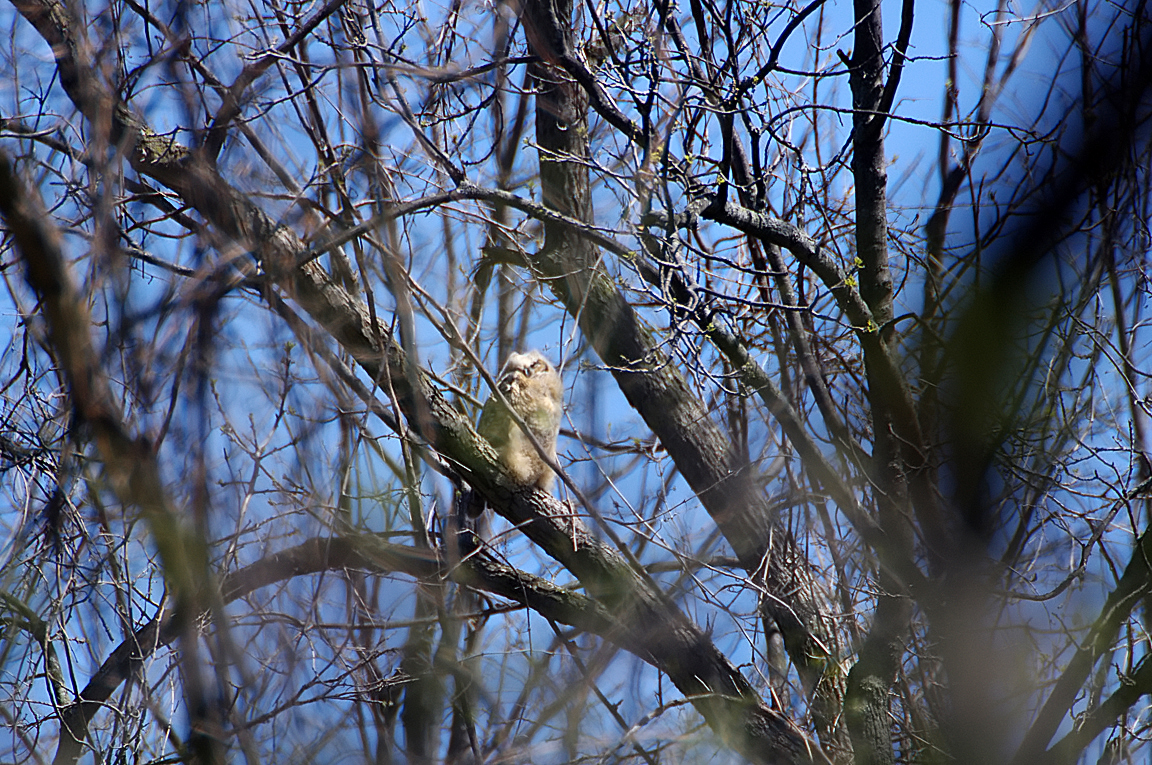
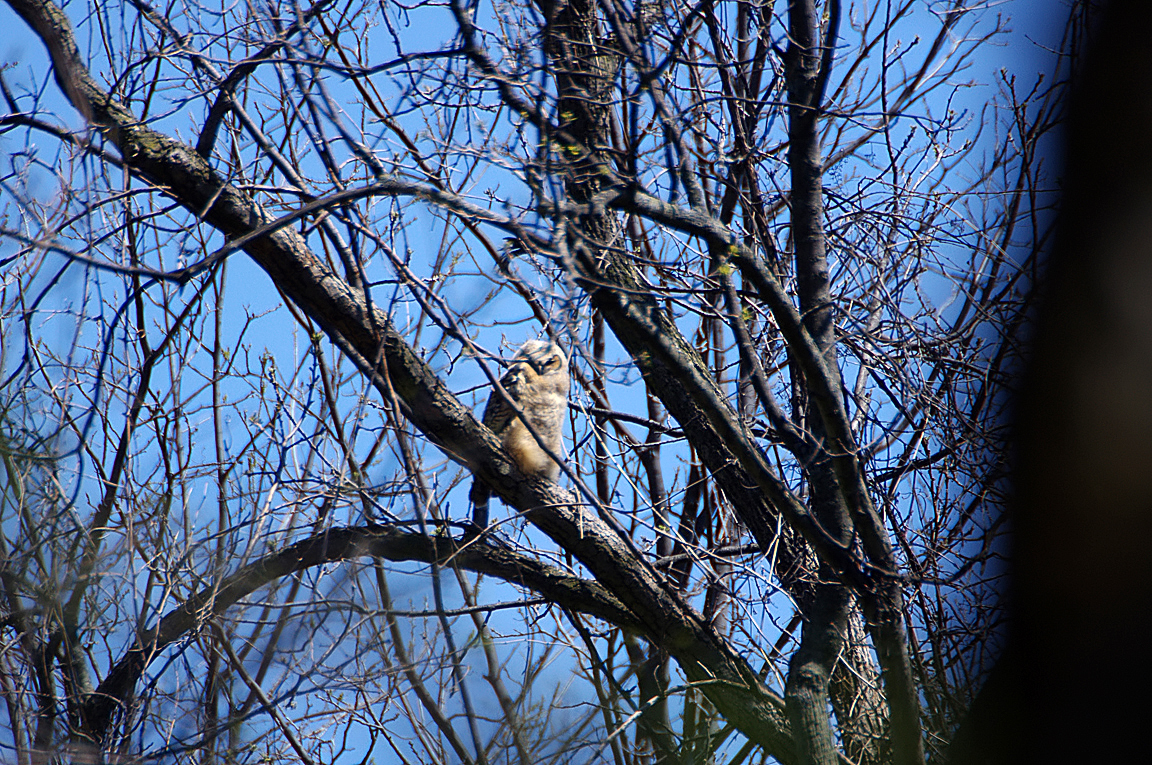
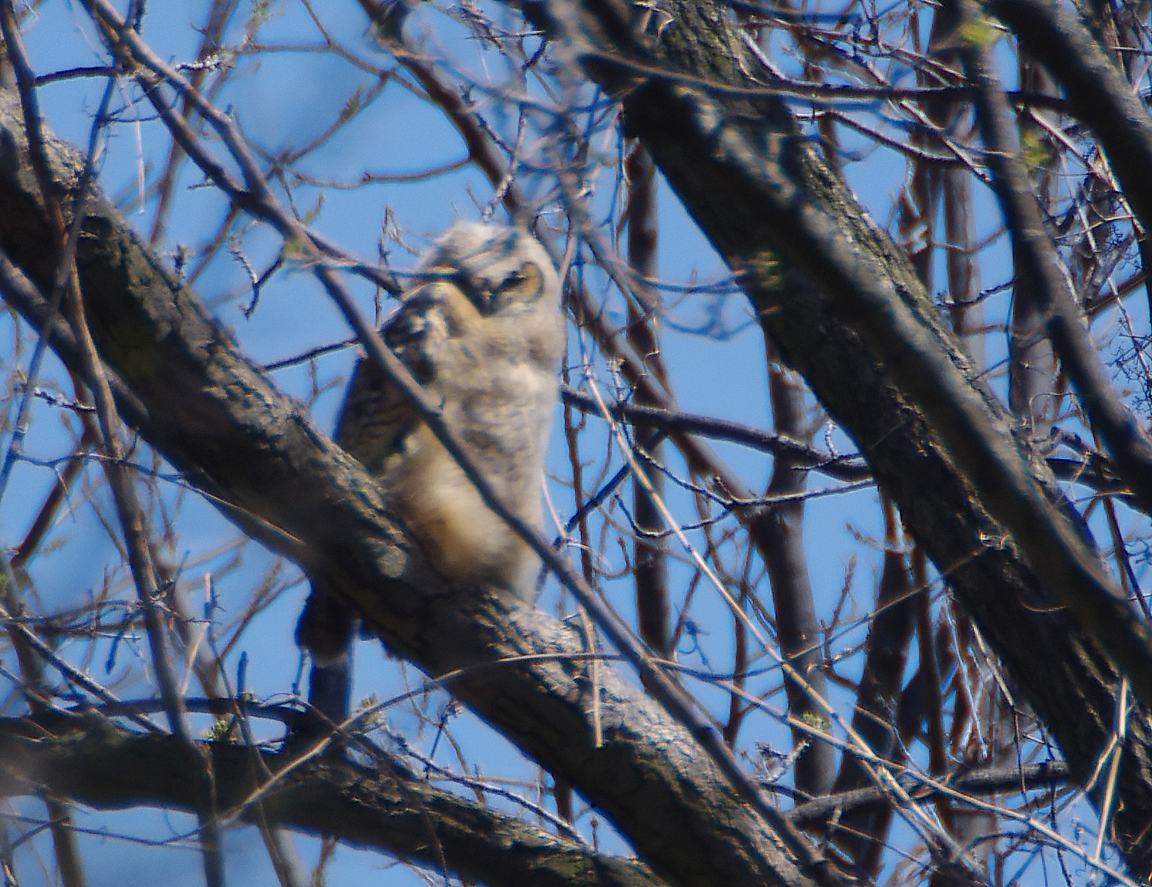
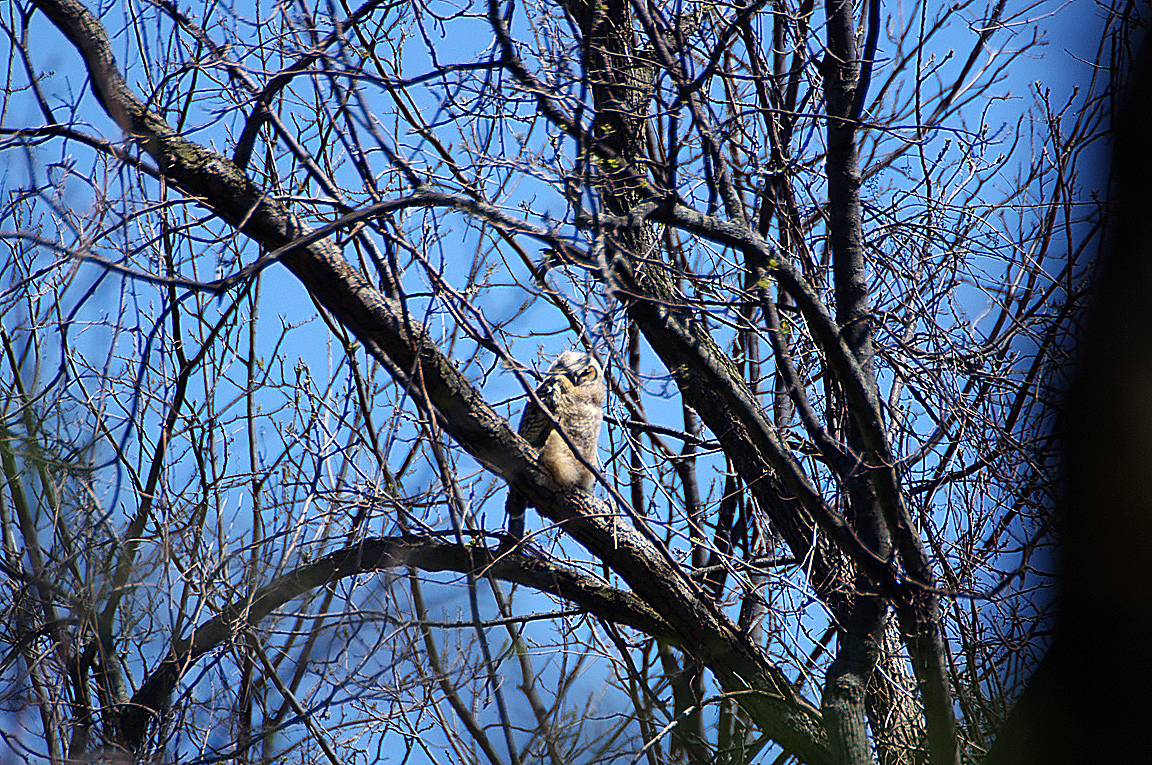
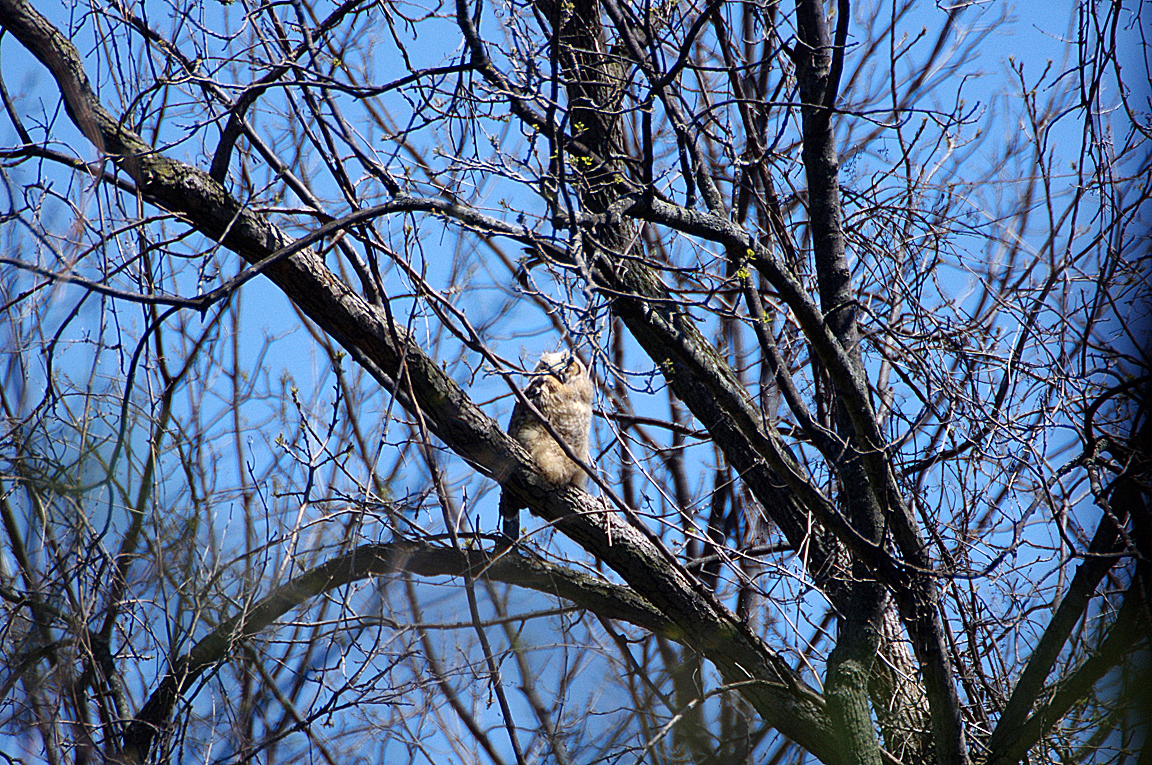
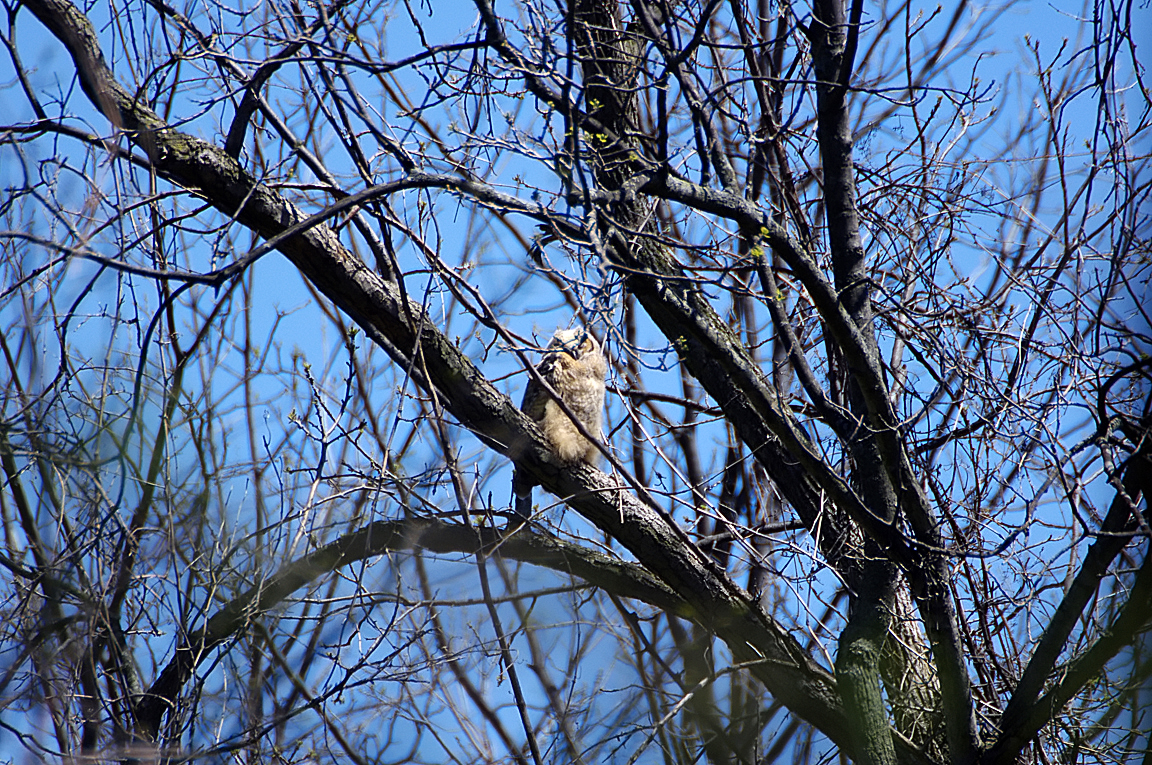
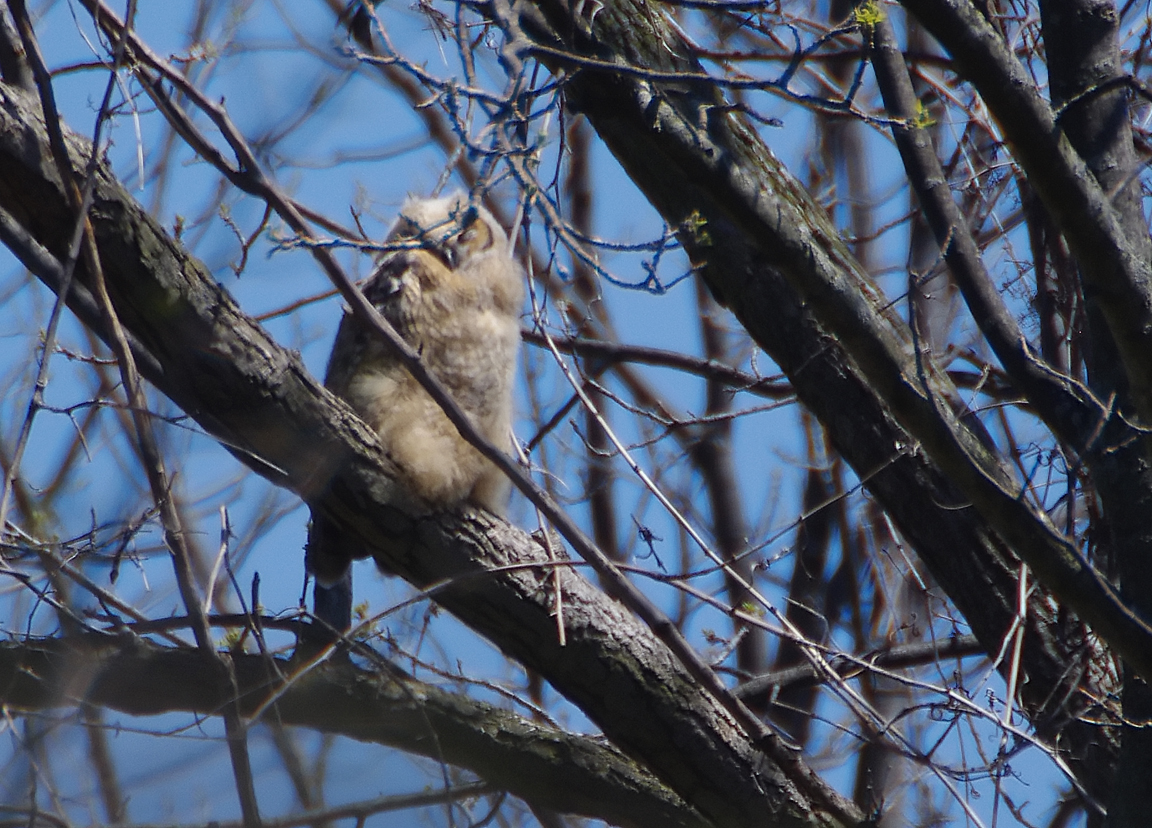
Great Horned Owl
|
| Bubo virginianus | |
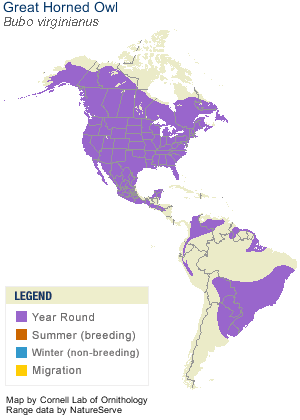
Found from the Arctic tundra to the tropical rainforest, from the desert to suburban backyards, the Great Horned Owl is one of the most widespread and common owls in North America.
Interesting Information
-
The Great Horned Owl is the only animal that regularly eats skunks.
-
The Great Horned Owl will take large prey, even other raptorial birds. It regularly kills and eats other owls, and is an important predator on nestling Ospreys. The reintroduction of Peregrine Falcons has been hampered in some areas by owls killing both adult and nestling falcons.
-
The Great Horned Owl is a regular victim of harassment from flocks of American Crows. Crows congregate from long distances to mob owls, and may continue yelling at them for hours. The enmity of the crows is well earned, however, as the owl is probably the most important predator on adult crows and nestlings.
-
Even though the female Great Horned Owl is larger than her mate, the male has a deeper voice. Pairs often call together, with audible differences in pitch.
-
A group of owls has many collective nouns, including a "bazaar", "glaring", "parliament", "stooping", and "wisdom" of owls.
-
In frigid areas, where larger prey cannot be eaten quickly, they may let uneaten food freeze and then thaw it out later using their own body heat.
-
The Great Horned Owl will eat birds ranging in size from kinglets to Great Blue Herons and regularly eat other owls.
-
The reintroduction of Peregrine Falcons has been hampered in some areas by owls killing both adult and nestling falcons.
Description
Adult Description
-
Length Range: 46-64 cm (18-25 in)
-
Weight: 1360 g (48 oz)
-
Size: Large (16 - 32 in)
-
Color Primary: Brown, Gray
-
Underparts: Red-brown with dark barring and white upper breast.
-
Upperparts: Dark brown with gray-brown mottling.
Sex Differences
Sexes Similar
Immature
Immature like adult. Fledges from nest while still downy around the head and without noticeable ear tufts.
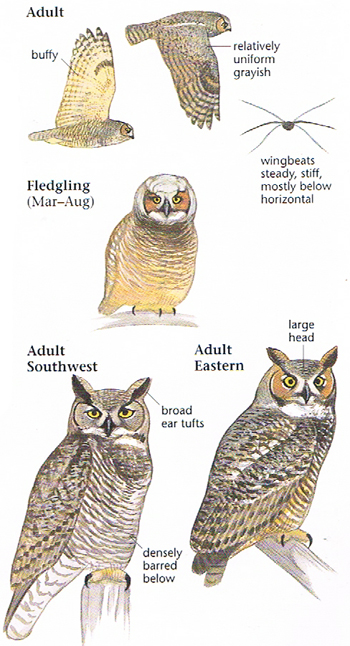
Photo taken from: The Sibley Field Guide by David Allen Sibley
© 2003 Cornell Lab of Ornithology
|
Habitat |
|
|
Behavior |
|
Hunts at night, mostly from perches next to open areas. |
|
Food |
|
Broad diet of animals, from small mammals to rabbits, geese, and herons. Some birds, amphibians, reptiles, and invertebrates, but mostly mammals. |
Taxonomy
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Subphylum: | Vertebrata |
| Class: | Aves |
| Order: | Strigiformes |
| Family: | Strigidae |
| Subfamily: | Striginae |
| Genus: | Bubo |
| Species: | Bubo virginianus |
| Subspecies: | Bubo virginianus algistus |
| Bubo virginianus elachistus | |
| Bubo virginianus heterocnemis | |
| Bubo virginianus lagophonus | |
| Bubo virginianus mayensis | |
| Bubo virginianus mesembrinus | |
| Bubo virginianus nacurutu | |
| Bubo virginianus nigrescens | |
| Bubo virginianus pacificus | |
| Bubo virginianus pallescens | |
| Bubo virginianus saturatus | |
| Bubo virginianus subarcticus | |
| Bubo virginianus virginianus |
Similar Species |
|
|
Bird Sound |
|
Call a deep hooting "hoo-h'HOO--hoo-hoo." Young make a loud, raspy screech. |
|
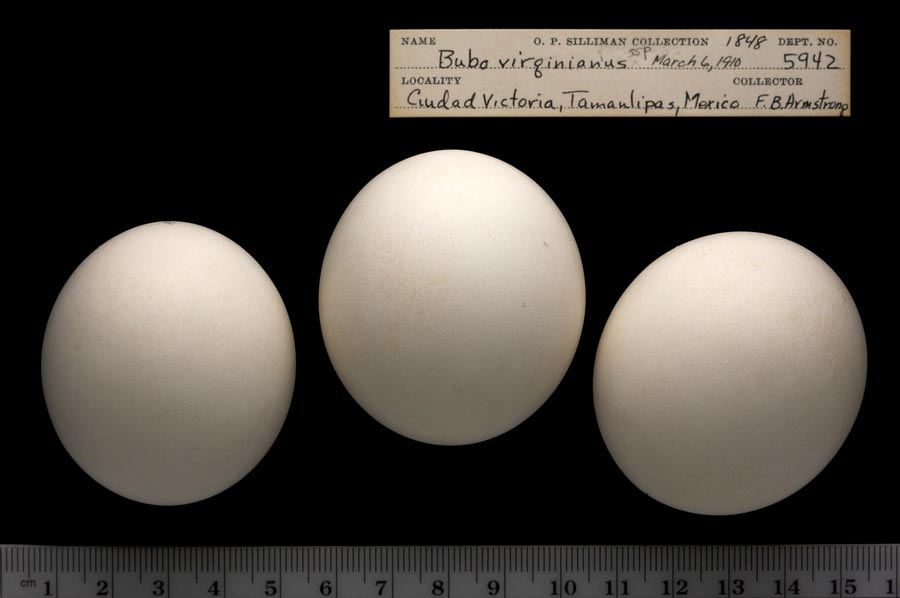
Eggs look like this |
|
Photo taken from: ARCTOS Collaborative Collection Management Solution |















