|
|
|
 |
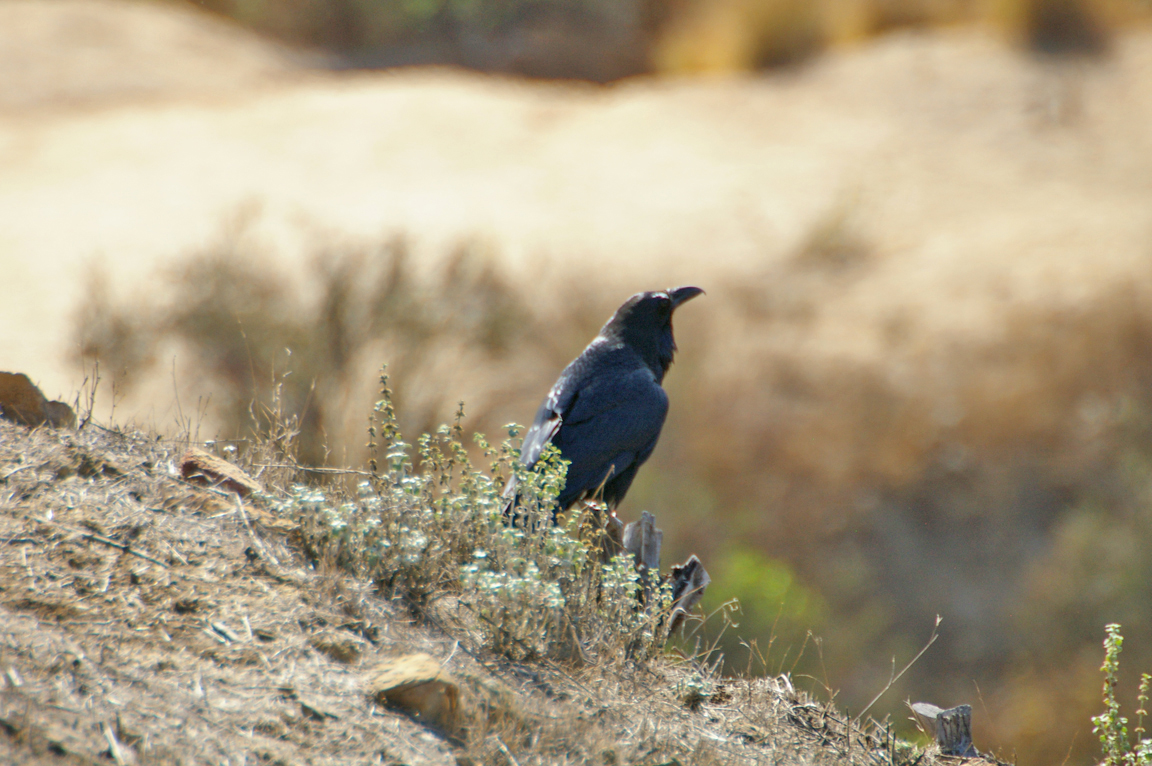
Common Raven
|
| Corvus corax | |
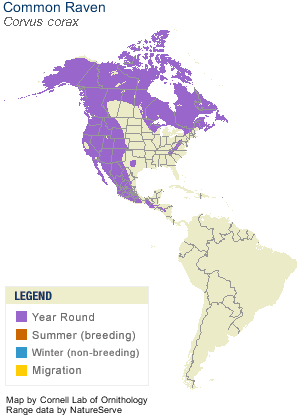
The largest of the songbirds, the Common Raven is one of the most widespread species in the world, found across North America and Eurasia, southward into Central America and northern Africa. Perhaps the smartest of all birds, the raven can survive in Arctic, temperate, and desert environments.
Interesting Information
-
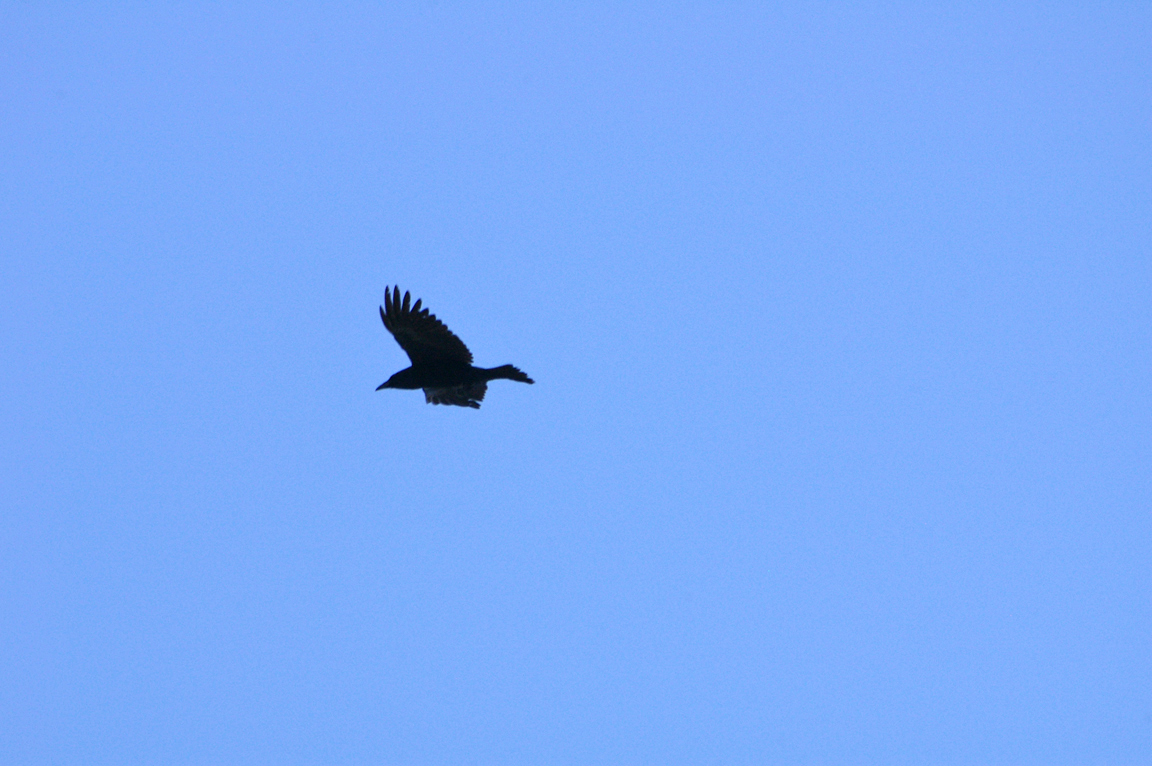
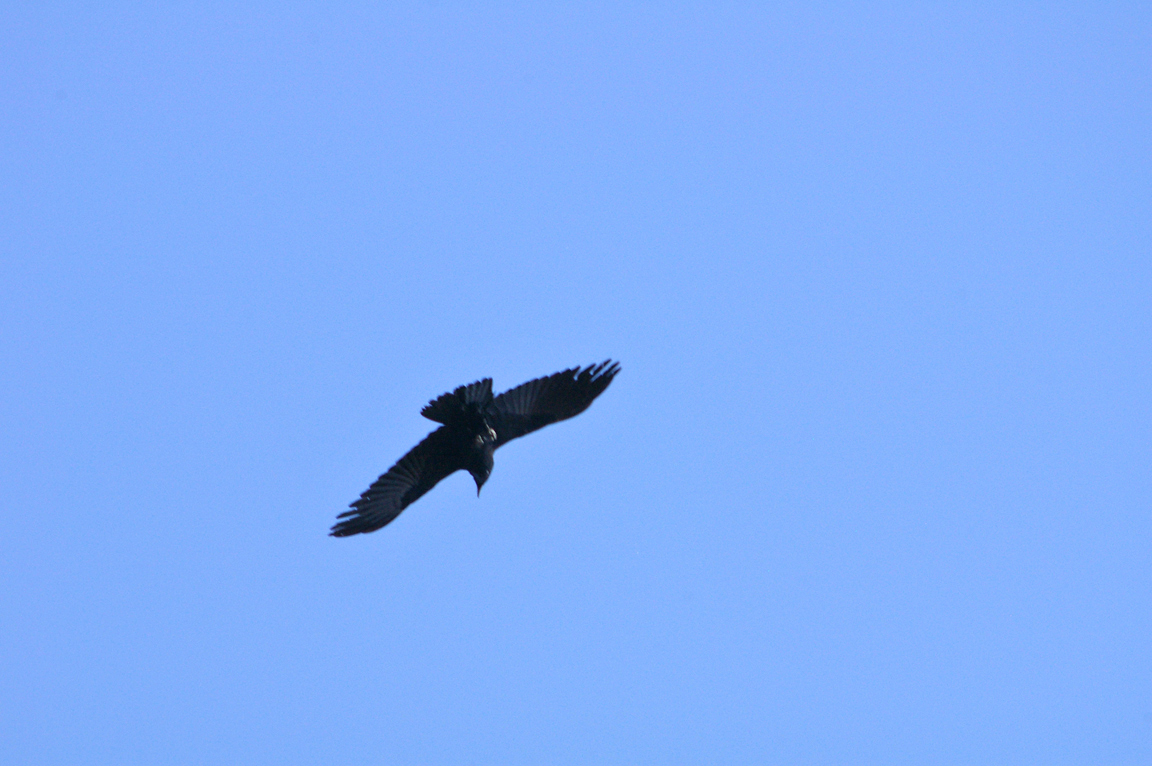
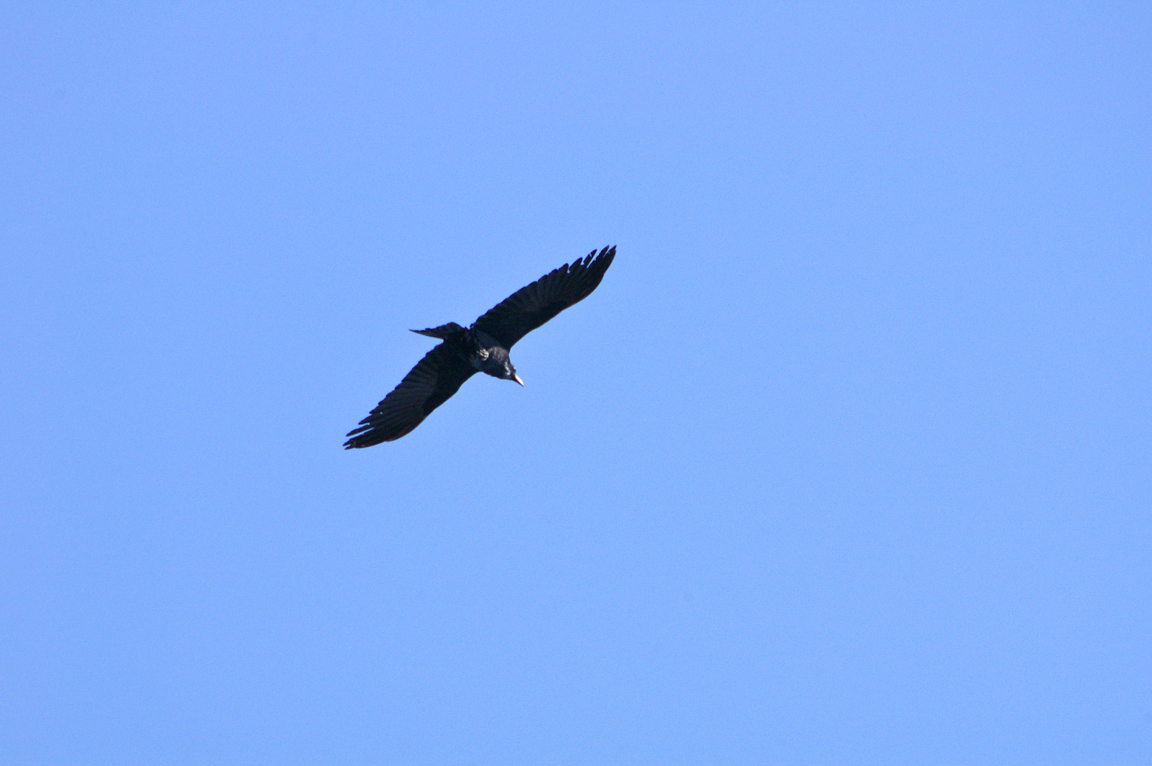
The Common Raven is an acrobatic flier. It frequently is seen to make rolls and somersaults in the air. It has even been observed flying upside down for as far as one kilometer (0.62 mi).
-
Breeding pairs of Common Ravens hold territories and try to exclude all other ravens throughout the year. In winter, young ravens finding a carcass will call other ravens to the prize. They apparently do this to overwhelm the local territory owners by force of numbers to gain access to the food.
-
The Common Raven often uses sheep wool to line its nest. When the female leaves the nest for a while she may cover the eggs with the wool.
-
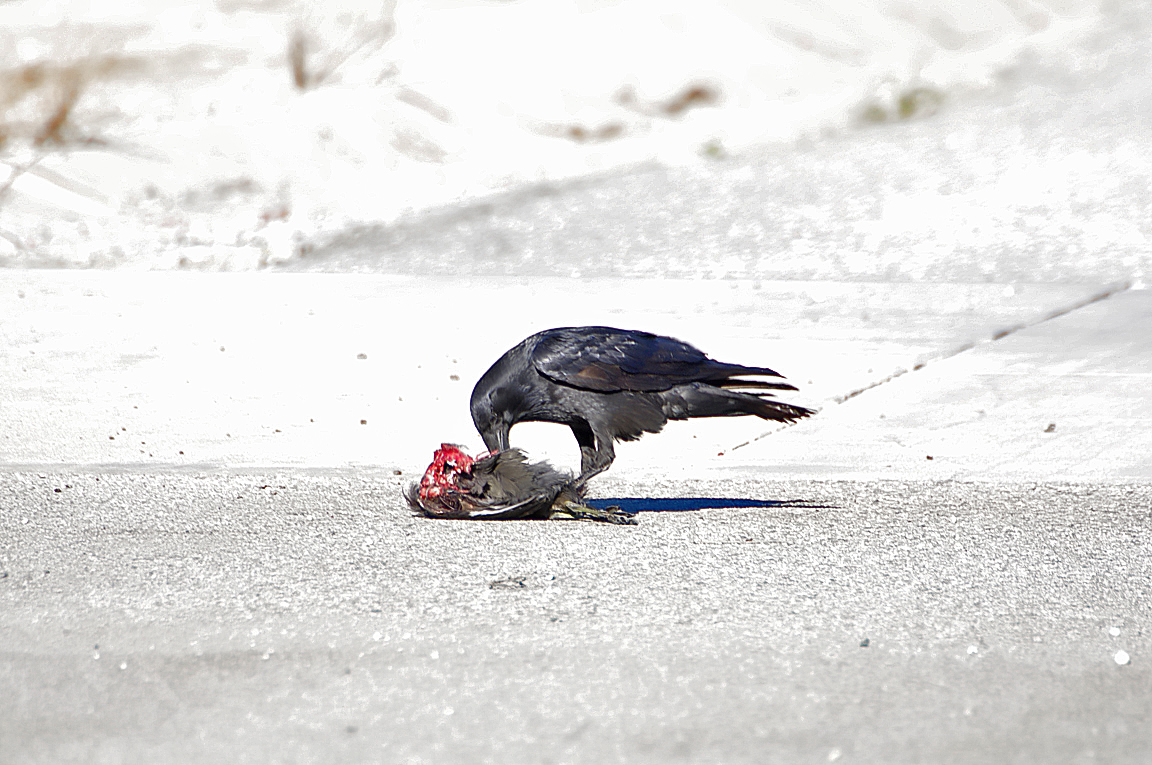
Increasing raven populations can have significant negative effects on the populations of some vulnerable prey species, such as desert tortoises and Least Terns. Ravens can cause trouble for people too. Ravens have been implicated in causing power outages by contaminating insulators on power lines, fouling satellite dishes at the Goldstone Deep Space Site, peeling radar absorbent material off buildings at the Chinal Lake Naval Weapons center, pecking holes in airplane wings, and stealing golf balls.
Description
Adult Description
-
Size: 56-69 cm (22-27 in)
-
Wingspan: 116-118 cm (46-46 in)
-
Weight: 689-1625 g (24.32-57.36 ounces)
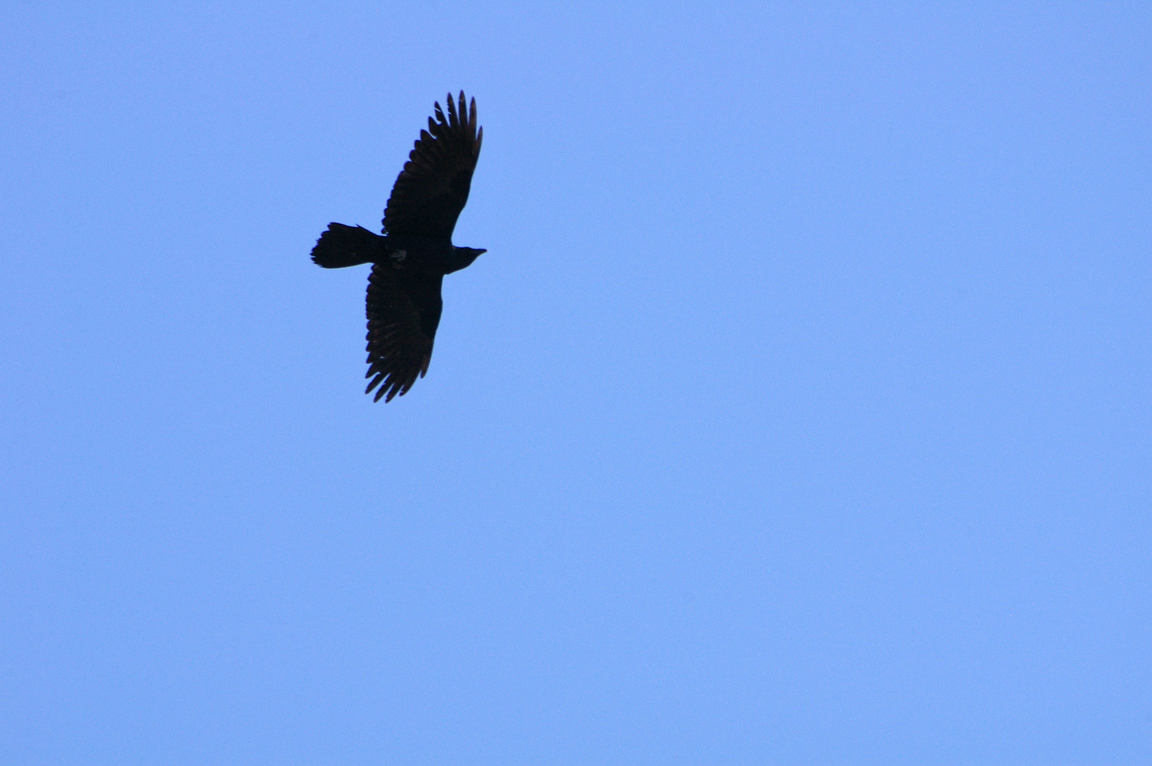
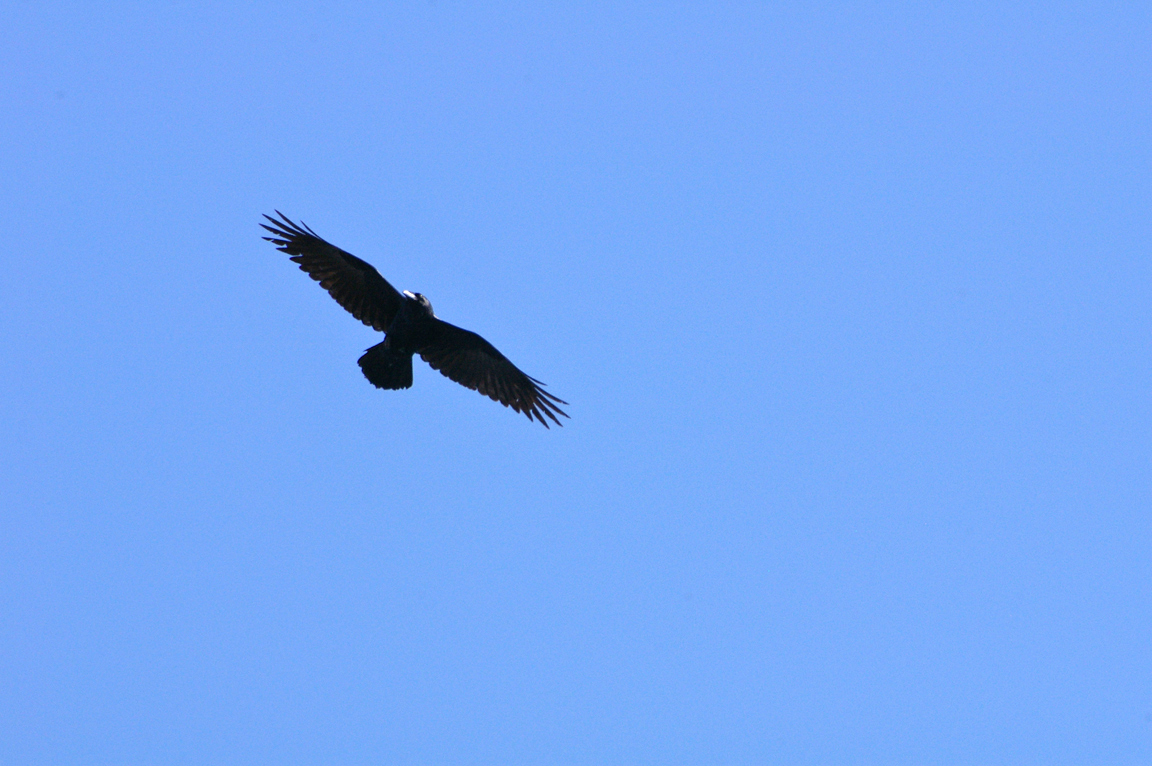
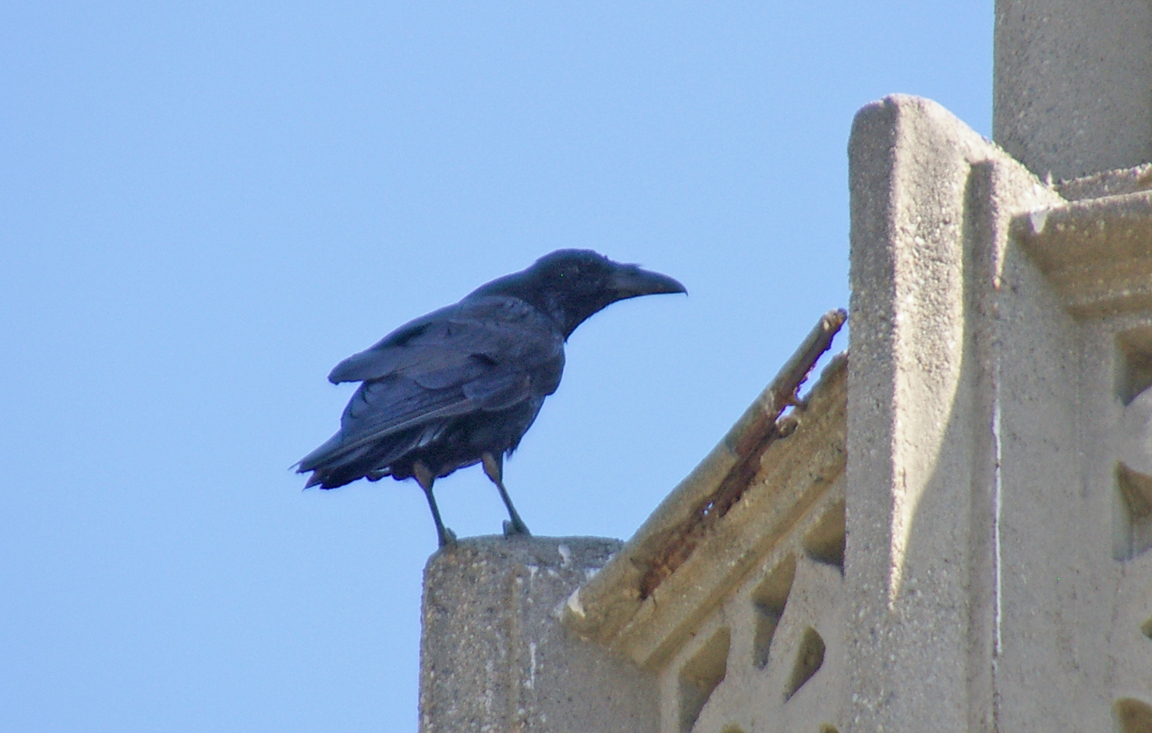
Very large crow.
All glossy black.
Relatively long, slightly curved bill.
Long, graduated or wedge-shaped tail.
Long pointed wings with obvious separation of primaries while soaring.
Elongated throat feathers.
Sex Differences
Sexes alike in plumage, but male slightly larger on average.
Immature
Juvenile similar to adult, but head and back feathers not glossy. Flight feathers become brown with wear.

Photo taken from: The Sibley Field Guide by David Allen Sibley
© 2003 Cornell Lab of Ornithology
|
Habitat |
|
Found in a broad range of habitats, including tundra, boreal forest, coniferous and deciduous forests, prairie and grassland, deserts, sea coasts, agricultural fields, towns, and cities. Prefers areas with cliffs for nesting. |
|
Behavior |
|
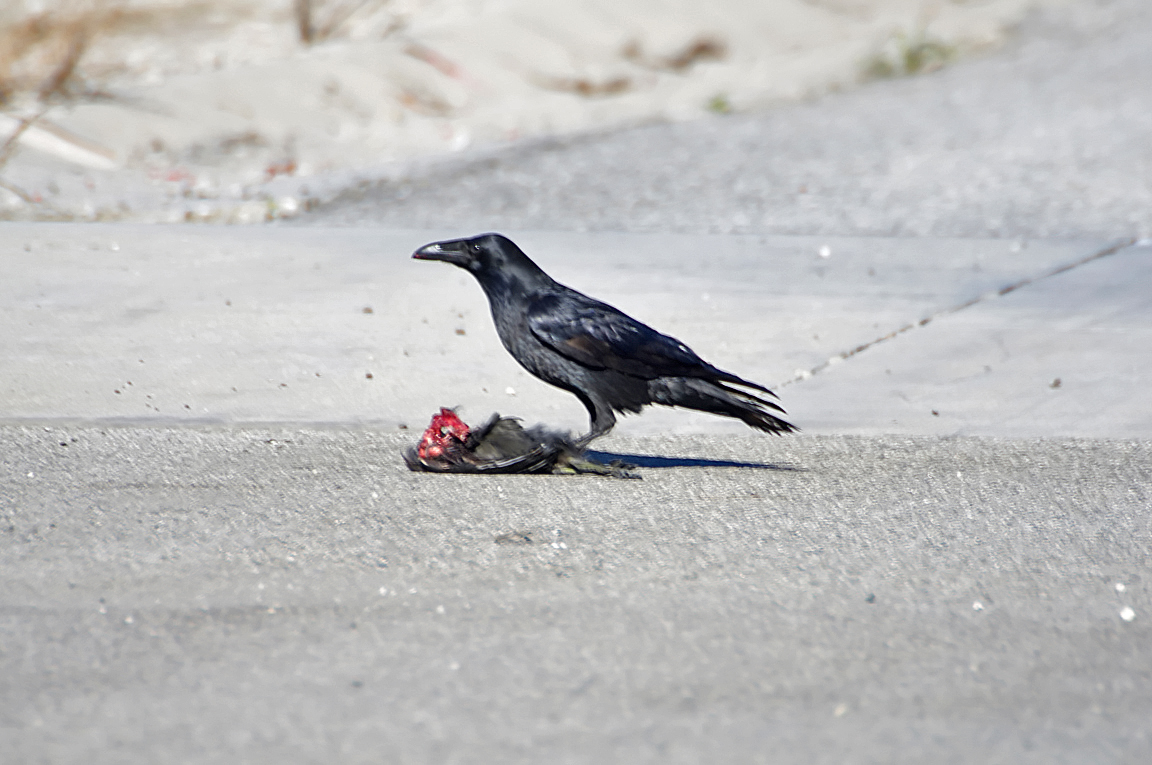
Follows predators to scavenge on leftovers. Patrols roadways for carrion. |
|
Food |
|
Omnivorous. Eats meat, eggs, insects, grain, fruit, garbage, and carrion. |
Taxonomy
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Subphylum: | Vertebrata |
| Class: | Aves |
| Order: | Passeriformes |
| Family: | Corvidae |
| Genus: | Corvus |
| Species: | Corvus corax |
| Subspecies: | Corvus corax clarionensis |
| Corvus corax corax | |
| Corvus corax principalis | |
| Corvus corax sinuatus |
Similar Species |
|
|
Bird Sound |
|
Common call a deep croak or hoarse "rrronk." Also a variety of sounds, including knocks and bell-like notes. |
|
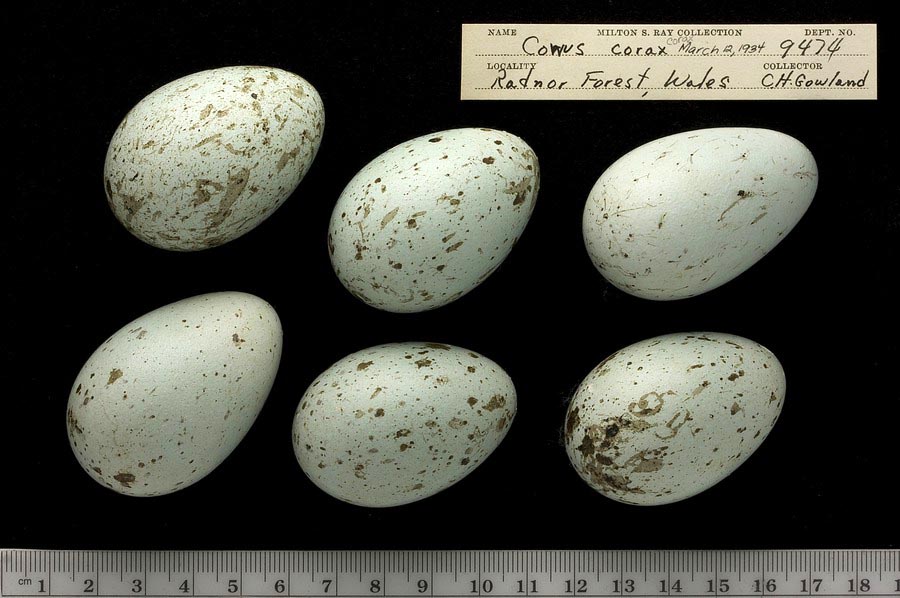
Eggs look like this |
|
Photo taken from: ARCTOS Collaborative Collection Management Solution |
















